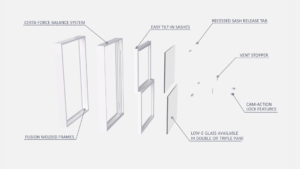
Anatomy of an Energy-Efficient Window
- Frame: constructed of vinyl, fiberglass, wood, or other composite frame materials.
- Multiple glass panes: typically have double- or triple-insulating glass with a high-performance Low-E coating for greater efficiency.
- Low-E coating: a film comprised of microscopic, metal or metallic oxide layers on the glass to keep heat inside in winter and out in summer.
- Inert gas fill: odorless, colorless, non-toxic gases such as argon or krypton inserted and sealed between the glass panes to improve the
insulating properties of the window. - Spacer system: ensure that the glass panes are the appropriate distance apart. These are constructed of aluminum, steel, composite, fiberglass, or vinyl. Warm-edge spacers lower a product’s overall U-value and reduce the likelihood of condensation.

 Single Hung
Single Hung
 Double Hung
Double Hung
 Casement
Casement
 Picture/Shapes
Picture/Shapes
 Sliding
Sliding
 Awning & Hopper
Awning & Hopper
 Bay & Bow
Bay & Bow
 Sliding Patio Doors
Sliding Patio Doors
 Entry Doors
Entry Doors